The Siberian Ice Maiden, also known as the Altai Princess or the Princess of Ukok, is one of the most remarkable archaeological discoveries in modern history.
She was unearthed in 1993 by Russian archaeologist Natalia Polosmak in the Ukok Plateau of Siberia, within the Altai Mountains.
This ancient mummy dates back approximately 2,500 years and is linked to the Pazyryk culture, a Scythian-era nomadic group known for their advanced skills in art, horse breeding, and warfare.
Key Details About the Siberian Ice Maiden
1. The Discovery
The Ice Maiden was found buried in a permafrost tomb, which naturally preserved her body, clothing, and grave goods.
Her tomb, a kurgan (burial mound), was filled with richly decorated items, including intricate textiles, wooden artifacts, and horse remains, signifying her high status.
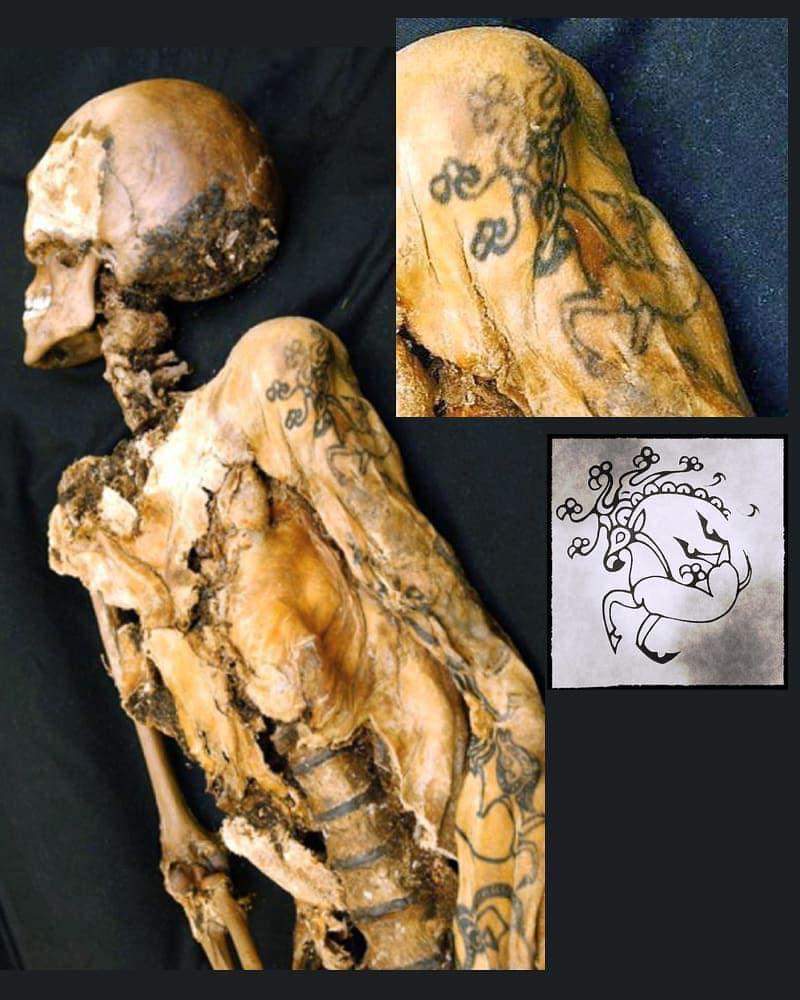
2. Tattoos on Her Body
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Ice Maiden is her tattoos, particularly a Scythian deer tattoo on her left shoulder.
The tattoo features fantastical creatures, with intricate details and curving antlers, blending animal motifs with mythical artistry.
These tattoos are considered some of the oldest known examples of body art, providing insights into the cultural and spiritual practices of the Pazyryk people.
3. Her Appearance and Clothing
The Ice Maiden was likely around 25-28 years old at the time of her death.She had shaven hair, suggesting she wore a wig, and her body was embalmed before burial.
Her clothing included a long woolen skirt, a silk blouse, and high felt boots, showcasing a sophisticated sense of style and craftsmanship.
4. Burial Customs
The Ice Maiden was buried with six horses, believed to be her companions in the afterlife.The presence of a cannabis-burning device and food offerings in her tomb suggests spiritual or ritualistic practices.
5. Her Cultural Significance
The Pazyryk culture, part of the larger Scythian tradition, valued tattoos as markers of identity, status, and possibly as spiritual symbols.
The Scythian deer tattoo, specifically, may have had protective or totemic significance, reflecting the interconnectedness of art, mythology, and spirituality.
6. Theories About Her Identity
Scholars debate whether she was a priestess, healer, or member of the Pazyryk elite. The elaborate nature of her burial points to a significant role within her society.
Her death may have been due to breast cancer and injuries from a fall, as modern analyses suggest.
7. Controversy and Preservation
The removal of the Ice Maiden from her tomb sparked controversy among the indigenous Altai people, who believe her presence disturbed sacred lands.
Efforts have been made to preserve her remains, which are now housed in a museum in the Altai Republic.
What Makes the Ice Maiden Unique?
The preservation of her tattoos provides a rare glimpse into the ancient art of tattooing, revealing its importance in early human history.
Her burial goods and tattoos offer valuable insights into the life, beliefs, and customs of the Pazyryk culture.
Her discovery has contributed significantly to the study of ancient Siberian nomadic peoples and their interactions with other cultures.
Cultural and Historical Impact
The Siberian Ice Maiden is not just an archaeological find but a time capsule that connects us to a rich and mysterious past.
Her tattoos have been compared to modern designs, showing how artistic expression transcends time. The debates about her significance continue to inspire interest in ancient cultures and their legacies.
